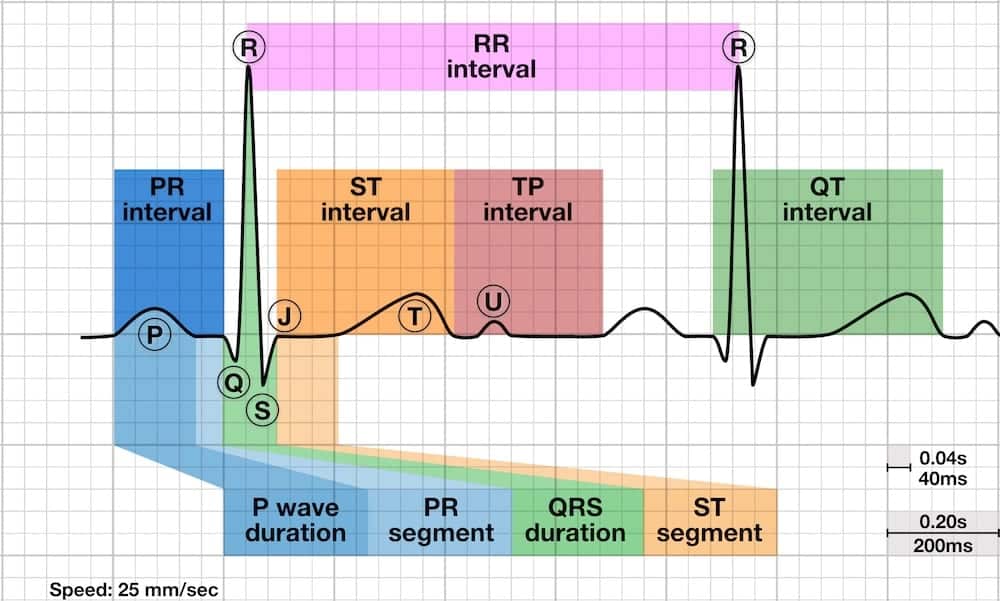
Notched Q Wave Ecg . a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. They are the result of absence of electrical activity. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads.
from litfl.com
They are the result of absence of electrical activity. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular.
QT Interval • LITFL • ECG Library Basics
Notched Q Wave Ecg Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. They are the result of absence of electrical activity. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads.
From ecgwaves.com
Other ECG changes in ischemia and infarction Cardiovascular Education Notched Q Wave Ecg They are the result of absence of electrical activity. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. Right bundle branch. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From litfl.com
QT Interval • LITFL • ECG Library Basics Notched Q Wave Ecg fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: They are the result of absence of electrical activity. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. the q wave is the. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From slidetodoc.com
How to Interpret an ECG Chapter 22 ECG Notched Q Wave Ecg by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. Right bundle branch block. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From ecgwaves.com
Other ECG changes in ischemia and infarction ECG learning Notched Q Wave Ecg Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From ecgwaves.com
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS Notched Q Wave Ecg by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From www.reddit.com
Does notched t wave automatically suggest LQTS2? ECG Notched Q Wave Ecg pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. by definition, a. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From www.vlr.eng.br
How To Read An ECG ECG Interpretation EKG Geeky Medics vlr.eng.br Notched Q Wave Ecg fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. They are the result. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From www.reddit.com
Notched t wave a concern? My ECGs usually look like the bottom row, but Notched Q Wave Ecg pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. They are the result of absence of electrical activity. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From ecgwaves.com
Early repolarization pattern on ECG (early repolarization syndrome Notched Q Wave Ecg the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg). Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From wtcs.pressbooks.pub
7.3 A Systematic Approach to Interpreting an ECG Nursing Advanced Skills Notched Q Wave Ecg fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. a q wave. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From litfl.com
J point ECG Interval • LITFL • ECG Library Basics Notched Q Wave Ecg Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular. by definition, a q wave on the. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From www.ahajournals.org
Abstract 2484 Fragmented QRS on a 12lead ECG is a Sign of Acute or Notched Q Wave Ecg Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
anterior STEMI q waves. Q waves are considered pathological if > 40 ms Notched Q Wave Ecg fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. pathologic q waves. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From ekgecho.de
The QRS complex ECG features of the Qwave, Rwave, Swave & duration Notched Q Wave Ecg fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: a q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From geekymedics.com
How to Read an ECG ECG Interpretation EKG Geeky Medics Notched Q Wave Ecg by definition, a q wave on the electrocardiogram (ecg) is an initially negative deflection of the qrs complex. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. fortunately, many causes of broad qrs can be identified by pattern recognition: They are the result. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Chest Pain and Qwaves in V1 and V2. Is there Notched Q Wave Ecg Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. the q wave is the. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Myocardial Infarction Ecg Strip Notched Q Wave Ecg They are the result of absence of electrical activity. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in the lateral leads. the q wave is the short initial downward stroke of the qrs complex formed during the beginning of ventricular. by definition, a q wave on. Notched Q Wave Ecg.
From litfl.com
J point ECG Interval • LITFL Medical Blog • ECG Library Basics Notched Q Wave Ecg pathologic q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. They are the result of absence of electrical activity. Right bundle branch block produces an rsr’ pattern in v1 and deep slurred s waves in the lateral leads. Left bundle branch block produces a dominant s wave in v1 with broad, notched r waves and absent q waves in. Notched Q Wave Ecg.